Abstract:Spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price in forex trading, used to measure trading costs. It is one of the main revenue sources for brokers and a direct reflection of market liquidity. Bid Price: The price at which the broker is willing to buy the base currency from you. Ask Price: The price at which the broker is willing to sell the base currency to you.
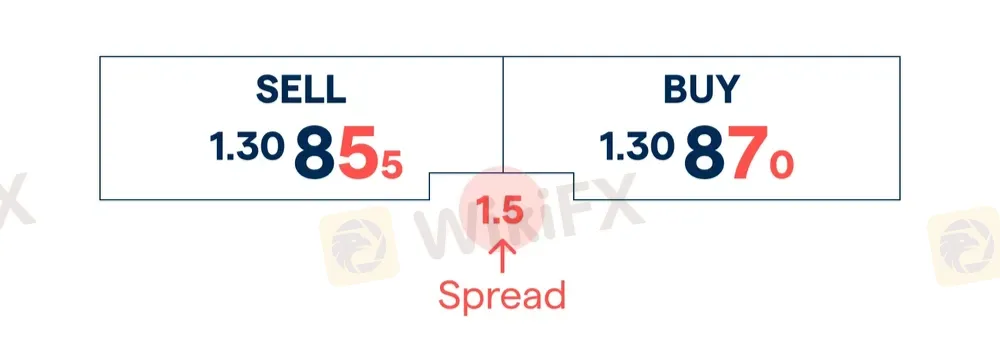
Spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price in forex trading, used to measure trading costs. It is one of the main revenue sources for brokers and a direct reflection of market liquidity.
Bid Price: The price at which the broker is willing to buy the base currency from you.
Ask Price: The price at which the broker is willing to sell the base currency to you.
Spread = Ask Price - Bid Price
The total cost of your trade is determined not only by the spread but also by the lot size (position size).
How to Calculate Forex Spread?
To calculate a forex spread, you must determine the difference between the bid (buy) and the ask (sell) prices. The formula is:
Ask price − bid price = spread
For example, if you trade GBP/USD at 1.3089/1.3091:
→ Spread = 1.3091 (ask) −1.3089 (ask) = 0.0002 (or 2 points).
[Photo]
The larger the spread calculated above, the higher the transaction cost. Traders generally prefer a tighter spread because it means lower trading costs.
During periods of high volatility or low liquidity in the forex market, spreads can widen significantly, and vice versa. For example:
- Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD have smaller spreads.
Emerging market currency pairs, such as the US dollar/South African rand, typically have wider spreads.

What Types of Forex Spreads Exist?
The type of spread you see on a trading platform depends on the forex broker and their revenue model. There are two main types of spreads:
- Fixed Spreads
- Variable (Floating) Spreads
Fixed spreads are typically offered by brokers operating as market makers or using a “trading desk” model. Variable spreads are provided by brokers that use a “no-dealing-desk” model, where they pass through market prices directly
What Are Fixed Spreads in Forex?
Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. Brokers offering fixed spreads often adopt a trading desk model where they aggregate large positions from liquidity providers and then break them down into smaller increments for retail traders to use. This means that the broker acts as the counterparty to the client's trade.
By utilizing a trading desk, forex brokers can offer fixed spreads because they control the prices shown to clients.
Fixed Spread: Pros and Cons
What Is a Floating Spread in Forex?
As the name suggests, variable spreads are constantly changing. In a floating spread, the difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices of a currency pair fluctuates continuously.
No-dealing-desk brokers obtain pricing for currency pairs from multiple liquidity providers and pass these prices directly to traders without interference. This means brokers cannot control the spread. Instead, spreads widen or contract based on:
- Supply and demand for the currency.
- Overall market volatility.
Typically, spreads widen during high-impact economic events (e.g., U.S. nonfarm payrolls releases) or periods of reduced liquidity (e.g., market holidays).
You might aim to buy EUR/USD at a 2-pip spread, but just as you click “buy,” the U.S. unemployment report is released, and the spread suddenly balloons to 20 pips! Similarly, erratic tweets about the dollar by former U.S. President Donald Trump could also trigger spread spikes.
Floating Spreads: Pros and Cons
Fixed Spreads vs. Variable Spreads: Which Is Better?
The choice of fixed spread and variable spread depends on the needs of the trader:
- Small accounts and low frequency traders generally benefit more from fixed point spreads due to predictable costs.
- Larger accounts and high-frequency traders (especially during periods of low volatility) may prefer variable spreads due to lower costs.
Traders who prioritize quick execution and avoiding quotes will find variable spreads advantageous.
Why Do Forex Spreads Change?
Forex spreads fluctuate when the difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices of a currency pair changes. Significant news announcements or events that increase market volatility can cause spreads to widen. One drawback of variable spreads is that if they expand sharply, your positions may be liquidated or margin calls may be issued.
The volatility of forex spreads is primarily driven by market conditions and broker operational models, with key factors including:
Market Volatility
During major news events (e.g., Nonfarm Payrolls, Federal Reserve meetings, geopolitical crises), liquidity decreases and prices become unstable, causing spreads to widen. In stable markets, ample liquidity and minimal price fluctuations typically result in narrower spreads. For example, a USD/JPY trade might widen from 2 pips to 5 pips following an unexpected interest rate decision.
Liquidity Levels
Major currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD) have tighter spreads due to high trading activity. In contrast, exotic pairs (e.g., USD/ZAR) or trades during low-liquidity periods (e.g., Asian session) face wider spreads due to insufficient liquidity.
Broker Pricing Models
- Market makers offer fixed spreads, which remain constant but may deviate from real-time market volatility.
- No-dealing-desk brokers provide variable spreads tied to liquidity provider pricing and market conditions.
Economic Event ImpactHigh-impact news, such as the 2023 Federal Reserve rate decision or U.S. CPI data releases, often triggers severe market volatility. For instance, after the Federal Reserve paused rate hikes in November 2023, anticipation of policy easing caused the EUR/USD spread to temporarily widen to 15 pips, before narrowing again due to hawkish comments from Chair Jerome Powell.
Trading Session Differences
- Session Overlaps: Spreads narrow during peak trading hours (e.g., London-New York overlap) but widen during low-volume periods (e.g., Asian session).
Forex Spread Trading Strategies
Peeling Strategy
Scalping trades are concentrated in highly liquid periods, such as the London-New York overlap, where the goal is to make a small profit (0.1-1 points per trade). Use limit orders to reduce slippage and set wider stop losses (20-30 points) to handle sudden market movements.
News-Based Strategy
This strategy takes advantage of the release of economic data (e.g., NFP, CPI), resulting in a spike in spreads and initial price momentum. Trade ahead of events and use broad stop losses (50-30 points) to prevent liquidity-driven reversals.
Range Trading Strategy
In a sideways market (e.g., EUR/USD daily chart), a trade is made between identified support and resistance levels. Use the RSI signal to enter/exit and tighten the stop loss if the range breaks out to avoid the wrong signal.
Carry Trading Strategy
Borrow in low-yielding currencies (such as the Japanese yen) and invest in higher-yielding assets (such as the Australian dollar) to profit from the interest rate differential. Monitor central bank policy changes to avoid sudden reversal of carry trades.
Breakthrough Strategy
Enter the trade after confirming a breakout (for example, above Bollinger band resistance) and validate the volatility expansion using the ATR indicator. Use trailing stop losses to lock in profits as the trend develops.
Event Arbitrage strategy
During a geopolitical crisis or central bank intervention, take advantage of price gaps between relevant markets (e.g., EUR/USD vs EUR/GBP). Use options to hedge against extreme volatility and limit position size to less than 1% of traded assets.
(For example, EUR vs USD vs EUR vs GBP). Hedged options and cap position size (≤1% equity).
FAQs
What is a Good Forex Spread?
A good forex spread is typically small, meaning the difference between the bid (buy) price and the ask (sell) price is minimal. For major currency pairs like EUR/USD, a spread of 1-3 pips is generally considered good.
What is a 1-Pip Spread?
A 1-pip spread means the difference between the bid price and the ask price is 1 pip, the smallest price movement in most currency pairs. For example, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1000 and the ask price is 1.1001, the spread is 1 pip (0.0001).
Why Do Forex Spreads Widen at 10 PM?
Forex spreads often widen at 10 PM GMT because major trading hubs (e.g., London) close, reducing market liquidity and trading activity. Lower liquidity makes it harder to match buyers and sellers, prompting brokers to widen spreads to manage their risk exposure.









