简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
The Different Ways To Trade Forex
Abstract:Since forex is so great, dealers concocted various ways of putting or conjecture in monetary forms. Among the most popular financial products are retail Forex, Spot FX, Forex Futures, Forex Options, Forex Trading Funds (or ETFs), Forex CFDs and Forex Spread Betting.
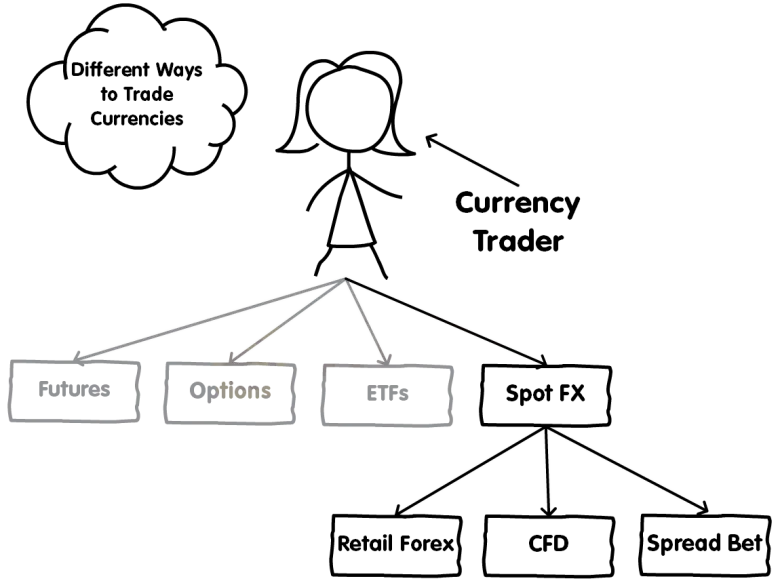
It's vital to specify out that we got the various ways that individual (“retail”) traders can exchange FX.
Other monetary instruments like FX trades and advances are not covered since they oblige institutional dealers.
With that far removed, how about we currently examine how you can participate in the realm of forex.
Currency Futures
Futures are agreements to trade a specific resource at a predefined cost on a future date (That's the reason they're called fates!).
A currency future is an agreement that subtleties the cost at which a money could be traded and sets a particular date for the trade.
Currency Futures were made by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) way back in 1972 when ringer bottoms and stage boots were as yet in style.
Since futures contracts are normalized and exchanged on a brought together trade, the market is extremely straightforward and very much controlled.
This implies that cost and exchange data are promptly accessible.
You can get familiar with CME's FX prospects here.
Currency Options
An “option” is a monetary instrument that gives the purchaser the right or the choice, however not the commitment, to trade a resource at a predefined cost on the choice's lapse date.
On the off chance that a merchant “sold” an option, the individual would be obliged to trade an asset at a particular cost at the lapse date.
Very much like futures, choices are additionally exchanged on a trade, like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), the International Securities Exchange (ISE), or the Philadelphia Stock Exchange (PHLX).
Nonetheless, the burden in exchanging FX choices is that market hours are restricted for specific choices and the liquidity isn't close to as extraordinary as the prospects or spot market.
Currency ETFs
A currency ETF offers openness to a solitary money or crate of monetary forms.
Currency ETFs permit customary people to acquire openness to the forex market through an oversaw store without the weights of putting individual exchanges.
Currency ETFs can be utilized to theorize on forex, enhance a portfolio, or support against money hazards.
Here is a rundown of the most prevalently exchanged money ETFs.
ETFs are made and overseen by monetary establishments that purchase and hold monetary forms in an asset. They then, at that point, offer portions of the asset to general society on a trade permitting you to purchase and exchange these offers very much like stocks.
Like currency options, the constraint in exchanging cash ETFs is that the market isn't open 24 hours. Additionally, ETFs are liable to exchanging commissions and other exchange costs.
Spot FX
The spot FX market is an “off-trade” market, otherwise called an over-the-counter (“OTC”) market.
The off-trade forex market is a huge, developing, and fluid monetary market that works 24 hours every day.
It's anything but a market in the conventional sense since there is no focal exchanging area or “trade”.
In an OTC market, a client exchanges straightforwardly with a counterparty.
In contrast to currency futures, ETFs, and (most) currency options, which are exchanged through incorporated business sectors, spot FX are over-the-counter agreements (private arrangements between two gatherings).
The majority of the exchanging is directed through electronic exchanging organizations (or phone).
The essential market for FX is the “interdealer” market where FX sellers exchange with one another. A seller is a monetary mediator that stands prepared to trade monetary standards whenever with its customers.
The interdealer market is otherwise called the “interbank” market because of the predominance of banks as Forex vendors.
The interdealer market is simply open to foundations that exchange enormous amounts and have an exceptionally high total assets.
This incorporates banks, insurance agencies, annuity reserves, enormous partnerships, and other huge monetary organizations deal with the dangers related with changes in currency rates.
In the spot FX market, an institutional trader is trading an understanding or agreement to make or take conveyance of a currency.
A spot FX exchange is a respective (“between two gatherings”) consent to truly trade one cash against another money.
This understanding is an agreement. This implies this spot contract is a limiting commitment to trade a specific measure of forex money at a value that is the “spot swapping scale” or the current conversion standard.
So assuming you purchase EUR/USD on the spot market, you are exchanging an agreement that determines that you will get a particular measure of euros in return for U.S dollars at a settled upon cost (or swapping scale).
It's essential to specify out that you are NOT exchanging the hidden monetary forms themselves, yet an agreement including the fundamental monetary forms.
Despite the fact that it's designated “spot”, the exchange isn't completely settle “on the spot”.
As a general rule, while a spot FX exchange is done at the current market rate, the real exchange isn't settled until two work days after the exchange date.
This is known as T+2 (“Today in addition to 2 work days”).
It implies that conveyance of what you trade ought to be finished inside two working days and is alluded to as the worth date or conveyance date.
For instance, a foundation purchases EUR/USD in the spot FX market.
The exchange opened and shut on Monday has a worth date on Wednesday. This implies that it'll get euros on Wednesday.
However, not all monetary standards settle T+2. For instance, USD/CAD, USD/TRY, USD/RUB and USD/PHP esteem date is T+1, which means one work day going ahead from today (T).
However, exchanging the genuine spot forex market isn't the place where retail brokers exchange.
Retail Forex
There is an auxiliary OTC market that gives a method for retailing (“more unfortunate”) traders to take an interest in the forex market.
Access is conceded by supposed “forex trading providers”.
Forex trading providers trade the essential OTC market for your benefit. They find the best accessible costs and afterward add a “markup” prior to showing the costs on their trading stages.
This is like the way that a retail location purchases stock from a discount market, adds a markup, and shows a “retail” cost to their clients.
Forex exchanging suppliers are otherwise called “forex brokers”. In fact, they are not brokers on the grounds that a merchant should just go about as an agent between a purchaser and a dealer (“between two gatherings”). However, this isn't true, in light of the fact that a forex trading supplier goes about as your counterparty. This implies assuming you are the purchaser, it goes about as the merchant. Also assuming that you are the dealer, it goes about as the purchaser. To save things straightforward for the present, we will in any case utilize the expression “forex broker” since that is the thing that a great many people know about yet it's essential to know the distinction.
Albeit a spot forex contract typically requires conveyance of money inside two days, by and by, no one takes conveyance of any cash in forex exchanging.
The position is “rolled” forward on the conveyance date.
Particularly in the retail forex market.
Keep in mind, you are really exchanging an agreement to convey the hidden money, rather than the actual cash.
It's not simply an agreement, it's a utilized agreement.
Retail forex brokers can't “take or make conveyance” on leveraged spot forex contracts.
Leverage permits you to control a lot of money for a tiny sum.
Retail forex brokers let you trade with leverage which is the reason you can open positions esteemed at multiple times how much the underlying required margin.
So with $2,000, you can open an EUR/USD exchange esteemed at $100,000.
Suppose you went short EUR/USD and needed to convey $100,000 worth of euros!
You'd not be able to settle the agreement in real money since you just have $2,000 in your record. You wouldn't have sufficient assets to cover the trade!
So you either need to close the exchange before it settles or “roll” it over.
To stay away from this problem of actual conveyance, retail forex brokers handles consequently “roll” customer positions.
At the point when a spot forex exchange isn't actually conveyed however endlessly continued onward until the trade is closed, it is known as a “rolling spot forex transaction” or “rolling spot FX contract”. In the U.S., the CFTC considers it a “retail forex exchange”.
This is the way you try not to be compelled to acknowledge (or convey) 100,000 euros.
Retail forex exchanges are finished off by going into an equivalent however inverse exchange with your forex broker.
For instance, assuming you purchased British pounds with U.S. dollars, you would finish off the exchange by selling British pounds for U.S. dollars.
This is likewise called counterbalancing or selling an exchange.
Assuming you have a position left open at the end of the work day, it will be naturally turned over to the following worth date to stay away from the conveyance of the currency.
Your retail forex broker representative will consequently continue to turn over your spot contract for you endlessly until it is shut.
The methodology of moving the cash pair over is known as Tomorrow-Next or “Tom-Next”, which means “Tomorrow and the following day.”
At the point when positions are turned over, this outcomes in either premium being paid or acquired by the broker.
These charges are known as a trade expense or rollover expense. Your forex dealer computes the charge for yourself and will either charge or credit your account balance.
Retail forex exchanging is viewed as speculative. This implies traders are attempting to “speculate” or make wagers on (and benefit from) the development of trade rates. They're not hoping to take actual ownership of the monetary forms they purchase or convey the monetary forms they sell.
Forex Spread Bet
Spread betting is a subsidiary item, which implies you don't take responsibility for fundamental resource yet speculate on whichever course you figure its cost will go up or down.
A forex spread bet empowers you to estimate on the future value bearing of a money pair.
A currency pair's cost being utilized on the spread bet is “inferred” from the money pair's cost on the spot FX market.
Your benefit or misfortune is directed by how far the market moves in support of yourself before you close your position and how much cash you have bet per “point” of value development.
Spread betting on forex is given by “spread betting providers”.
Tragically, assuming you live in the U.S., spread betting is thought of as unlawful. In spite of being controlled by the FSA in the U.K., the U.S. considers spread wagering to be web betting which is presently illegal.
Forex CFD
A Contract for difference (“CFD”) is a monetary subsidiary. Subordinate items track the market cost of a hidden resource so merchants can speculate on whether the cost will rise or fall.
The cost of a CFD is “inferred” from the hidden resource's cost.
A CFD is an agreement, commonly between a CFD provider and a trader, where one party consents to pay the other the distinction in the worth of a security, between the opening and shutting of the exchange.
All in all, a CFD is fundamentally a bet on a specific resource going up or down in esteem, with the CFD provider and you concur that whoever wins the bet will pay the other the contrast between the resource's cost when you enter the exchange and its cost when you exit the trade.
A forex CFD is an understanding (“contract”) to trade the distinction in the cost of a currency pair from when you open your position versus when you close it.
A currency pair's CFD cost is “determined” from the cash pair's cost on the spot FX market. (Or if nothing else it ought to be. If not, what is the CFD provider putting together its cost with respect to?
Exchanging forex CFDs offers you the chance to exchange a cash pair in the two headings. You can take both long and short positions.
Assuming the value moves in your picked heading, you would create a gain, and in the event that it moves against you, you would make a misfortune.
In the EU and UK, controllers concluded that “rolling spot FX contracts” are unique in relation to the conventional spot FX contract.
The primary explanation being is that with moving spot FX contracts, there is no aim to at any point take genuine actual conveyance (“take proprietorship”) of a cash, its motivation is to just estimate on the value development in the hidden money.
The goal of exchanging a rolling spot FX contract is to acquire openness to value variances connected with the basic money pair without really possessing it.
So to make this separation understood, a moving spot FX contract is controlled as a CFD. (In the U.S., CFDs are unlawful so it's known as a “retail forex exchange”)
Forex CFD exchanging is given by “CFD providers”.
Outside the U.S., retail forex exchanging is generally finished with CFDs or spread wagers.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
WikiFX Broker
Currency Calculator






